Combination of Tetrahydrobiopterin and Arginine/ ± Arginase Inhibitors for the Treatment of COVID-19
Application
A novel drug combination to address acute arginine/BH4 dysregulation that develops with COVID-19 and MIS-C infection.
Key Benefits
- Potential to improve outcomes of those infected with COVID-19 with few side effects.
- Repurposing opportunity with the combination of two approved drugs (tetrahydrobiopterin and arginine).
- Addresses arginine dysregulation that occurs in COVID-19 infection and MIS-C.
Market Summary
Coronavirus (COVID-19) is an infectious disease that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome. The majority of those infected with COVID-19 experience mild to moderate respiratory illness and recover without requiring special treatment. However, the elderly and those who are immunocompromised are substantially more likely to develop severe illness leading to death. Although the FDA has authorized several vaccines to prevent COVID-19 infection, there has been significant resistance to vaccination and limited treatment options are available for those who are already infected.
Technical Summary
This invention describes methods of combining tetrahydrobiopterin, arginine, and/or arginase inhibitors for the treatment of the complications of COVID-19 infection. In an observational study, arginine levels in adult and pediatric patients with COVID-19 were reduced compared to healthy controls. The low arginine bioavailability may contribute to immune dysregulation and endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19. Decreased levels of nitric oxide is associated with endothelial dysfunction. Tetrahydrobiopterin serves as a cofactor for nitric oxide synthase and so increasing levels of tetrahydrobiopterin could counteract the endothelial dysfunction associated with COVD-19 infection. Hence, the administration of tetrahydrobiopterin and arginine and/or arginase inhibitor therapeutic agents may be a viable treatment modality for those with moderate to severe COVID-19 infection.
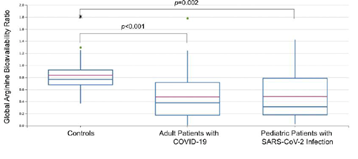 Figure 1: Decreased arginine bioavailability in COVID-19 patients.
Figure 1: Decreased arginine bioavailability in COVID-19 patients.
Publication: Rees, C. et al., Altered amino acid profile in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, PNAS, June 22, 2021 118 (25) e2101708118
Patent Information
| App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Patent Status |
| Nationalized PCT - Foreign |
EP |
22776727.4 |
|
3/25/2022 |
|
Pending |
| Nationalized PCT - United States |
United States |
18/284,236 |
|
9/26/2023 |
|
Pending |
|
|

