Application
Method to enhance the affinity of spherical nucleic acids for their targets.
Key Benefits
- Facile method for molecular printing on surface of NP.
- Massive improvement of SNA’s binding affinity to the target can provide strategies in applications for therapeutics and diagnostics.
- May maximize DNA density on the NP surface.
Market Summary
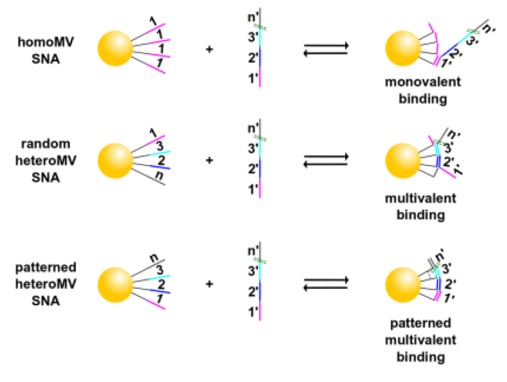
Spherical nucleic acids (SNAs) are a type of DNA nanostructure comprised of a dense arrangement of spherically-oriented oligonucleotides. Their enhanced affinity to nucleic acid targets, improved cellular uptake and nuclease resistance enable their application in sensing and therapeutics. The density, length and spatial alignment of oligos affect the binding affinity of a SNA, but simply increasing the density or length will not necessarily improve the target binding or affinity advantage. Approaches that further boost the affinity of SNAs are highly desirable for genetic-based therapeutic and diagnostic applications.
Technical Summary
Inventors have developed a method to control the position of a series of unique oligonucleotides on the nanoparticle surface to enable effective multivalent binding to a DNA target. This new method to engineer spherical nucleic acids, the integration of molecular printing and heteromultivalency into nucleic acid nanostructures, massively improves their affinity to targets and offers an approach to bind long nucleic acid targets (~90 nt) with high affinity. This approach to engineering spherical nucleic acids presents many possible applications for therapeutics and diagnostics including molecular diagnostics, CNS drug nanoparticles, intracellular gene regulation and intracellular probe.
Developmental Stage
A molecular printing method has been developed.
Publication: Deal, B. R. et al. (2020). J. Am. Chem. Soc., 142(21), 9653-9660.

