DNA Machines Enhance SNP Analysis Efficiency
Application
DNA-based machines that roll rather than walk and can be used for single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis.
Key Benefits
- Unique "rolling" cogwheel-like mechanism allows directional motion without a track or external guidance.
- Micron-sized cargo travels large distances; can be visualized using a smartphone camera equipped with an inexpensive lens.
- Moves up to 1,000 times faster than conventional DNA-based motors.
Market Summary
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) genotyping is the screening and analysis of genetic variations of SNPs in the genome of various species. SNPs are commonly present in all species including humans. SNP genotyping and analysis technology can analyze thousands of SNPs and has the potential for whole-genome genotyping. DNA-based machines have potential in several applications and industries. Unfortunately, DNA-based walkers are challenging to work with due to their low fidelity and slow rates. A new class of DNA-based machines with high fidelity and faster rates can significantly improve performance of applications ranging from next generation sensors to drug delivery platforms and biological computing.
Technical Summary
Inventors at Emory University have developed a DNA-based machine that can walk by converting chemical energy into controlled motion. This invention shows the first experimental demonstration of self-avoiding motion in DNA walking machines. The motor consists of a DNA-coated spherical particle that hybridizes to a surface modified with complementary RNA. The particle moves upon the addition of RNase H, which selectively hydrolyzes hybridized RNA but not single stranded RNA. This unique cogwheel-like mechanism allows directional motion without the need of a patterned track or external electromagnetic field. Because this new class of DNA-based machines roll rather than walk, they are able to surpass the maximum speed of existing DNA motors by three-orders of magnitude. This technology can serve as a new and powerful tool in SNP genotyping, as well as other applications in diagnostics, drug delivery, and biomaterials.
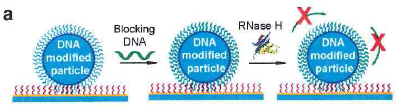
Developmental Stage
Proof of concept has been demonstrated in a laboratory setting.
Patent Information
| App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Patent Status |
| Utility (parent) |
United States |
15/332,007 |
10,738,349 |
10/24/2016 |
8/11/2020 |
Issued |
| Divisional |
United States |
16/922,449 |
11,884,967 |
7/7/2020 |
1/30/2024 |
Issued |
|
|